Introduction to Digital Identity Blockchain
In today’s digital economy, the concept of digital identity has become integral for secure and efficient online interactions. A digital identity covers the information that computer systems use to represent an external agent, such as an individual, organization, or device. As our reliance on digital platforms grows, the need for secure, reliable, and user-controlled identity systems becomes increasingly critical.
As Bob Greifeld, Nasdaq Chief Executive aptly said, “The blockchain is the biggest opportunity set we can think of over the next decade or so.” This highlights the transformative potential of blockchain technology, particularly in the realm of digital identity.
Blockchain technology, renowned for its decentralized and secure nature, offers a revolutionary approach to digital identity management. By leveraging blockchain, digital identities can be created, managed, and verified in a tamper-proof and transparent manner. This enhances security and privacy and empowers users with greater control over their personal data. Blockchain-based digital identity systems mitigate the risks associated with traditional centralized identity management, such as identity theft, data breaches, and unauthorized data sharing.
The integration of blockchain in digital identity systems marks a significant shift towards a more decentralized and user-centric model. This evolution is crucial for addressing the shortcomings of existing identity management frameworks and for paving the way towards more secure and private digital interactions. To understand how this innovative approach works, we need to delve into the mechanics of decentralized identity and explore its key components.
How Decentralized Identity Works
Decentralized identity represents a significant shift from traditional, centralized identity systems by putting control back into the hands of individuals. At the heart of decentralized identity systems are Decentralized Identifiers, which are unique, self-owned identifiers that allow users to create and manage their identities independently.
The creation and management of decentralized identities involve several steps:
- Generation of a DID: The user generates a DID along with its associated cryptographic keys. This process is typically facilitated by a DID management application or service.
- Registration on a Decentralized Network: The DID and its public key are registered on a decentralized network, such as a blockchain. This registration process ensures that the DID can be publicly resolved and verified by others.
- Issuance of Verifiable Credentials: Entities issue VCs to the user, who can then store these credentials in their identity hub. Each credential is cryptographically signed by the issuer, ensuring its authenticity and integrity.
- Verification of Identity: When the user needs to prove their identity or a specific attribute, they present the relevant VC to the verifier. The verifier uses the public key associated with the DID to cryptographically verify the credential, ensuring it has not been tampered with.
- Data Sharing and Consent Management: Users have complete control over their personal data and can manage consent for data sharing through their identity hub. They can choose to share specific pieces of information with service providers, and revoke access when necessary.
This architecture of decentralized identity systems provides a robust, secure, and privacy-preserving framework for managing digital identities. By leveraging blockchain technology and cryptographic methods, decentralized identity empowers individuals with control over their personal information, ensuring a higher level of trust and security in digital interactions.
Benefits of Blockchain-Based Digital Identity
The integration of blockchain technology into digital identity systems offers a multitude of benefits that address the limitations of traditional identity management frameworks. By leveraging the inherent properties of blockchain, such as decentralization, immutability, and cryptographic security, blockchain-based digital identity systems provide enhanced privacy, security, and user control. Here are the key benefits in detail:
| Benefit | Description |
| Privacy and Consent Management | Users have complete control over their personal data and can decide who has access to it and under what conditions. Verifiable Credentials (VCs) enable selective disclosure, protecting user privacy by sharing only necessary information. |
| Enhanced Security | Each identity is linked to a unique cryptographic key pair, ensuring only the rightful owner can manage it. The decentralized nature of blockchain reduces the risk of identity theft and data breaches by eliminating single points of failure. |
| Prevention of Identity Fraud | The immutable and transparent nature of blockchain ensures that identity data cannot be tampered with. Verifiable Credentials provide cryptographic validation, enhancing the integrity of identity verification processes. |
| Traceable and Auditable Transactions | Every identity-related interaction is recorded on the blockchain, creating an auditable trail for verifying the authenticity and integrity of transactions. This feature aids in regulatory compliance and forensic investigations. |
| User Empowerment and Sovereignty | Blockchain-based systems give users full control over their identities, allowing them to manage their data and access permissions independently, fostering greater trust and confidence in digital interactions. |
| Interoperability and Portability | Blockchain identities can be universally recognized and verified across multiple platforms. Users can seamlessly transfer their identity data between service providers, ensuring compliance with data portability regulations like GDPR. |
| Cost Efficiency | Blockchain technology reduces the need for intermediaries and redundant verification processes, lowering operational costs for organizations while improving the efficiency and accuracy of identity management. |
Key Components of Blockchain Identity Systems
Blockchain identity systems are built on a foundation of advanced technologies and standards designed to ensure security, privacy, and user control. These systems leverage several key components to create a robust and reliable framework for digital identities. Understanding these components is crucial for grasping the full potential of blockchain-based identity solutions.
Key Components of Decentralized Identity Systems
Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs): DIDs are a new type of identifier that enable verifiable, self-sovereign digital identities. Unlike traditional identifiers issued and controlled by centralized authorities, DIDs are created, owned, and managed by the individual user. These identifiers are globally unique and can be resolved using decentralized systems.
Public Key Infrastructure (PKI): Central to the security of DIDs is public key cryptography. Each DID is associated with a pair of cryptographic keys: a public key that can be shared with others and a private key that is kept secret by the owner. This cryptographic underpinning ensures that only the rightful owner of the DID can control it and sign transactions or claims.
Verifiable Credentials (VCs): VCs are digital statements issued by an entity (e.g., an employer, university, or government) that can be cryptographically verified. These credentials can include information such as professional qualifications, identity documents, or health records. VCs enable identity verification without the need to reveal unnecessary personal information, thereby preserving user privacy.
Identity Hubs: These are secure data storage services that interact with DIDs. Identity hubs store, manage, and provide access to personal data associated with a DID, ensuring that users have control over their data. They facilitate interactions between different decentralized identity components and allow users to share their data with service providers securely.
Universal Resolvers: These are tools or services that can resolve DIDs across different decentralized systems. Universal resolvers ensure interoperability between various DID methods and decentralized identity systems, allowing for seamless identity verification across different platforms.
Use Cases of Blockchain Digital Identity
Blockchain-based digital identity systems offer transformative solutions across various sectors by enhancing security, privacy, and efficiency. These systems address the limitations of traditional identity management frameworks and provide robust mechanisms for identity verification and data integrity. Below are detailed use cases demonstrating the versatility and impact of blockchain digital identity, accompanied by real-world examples.
Secure Identity Verification for Banking and Finance
In the banking and finance sector, blockchain-based digital identities streamline the identity verification process, reducing fraud and enhancing customer experience. Traditional Know Your Customer (KYC) processes are often time-consuming and costly. Blockchain technology can automate and secure these processes, allowing for faster and more reliable verification.
Government Services and Public Administration
Blockchain digital identities can revolutionize the way citizens interact with government services. By providing secure and tamper-proof digital identities, governments can offer streamlined services, reduce bureaucratic inefficiencies, and enhance trust in public administration.
Healthcare and Patient Data Management
In the healthcare sector, blockchain-based digital identities ensure secure access to patient data, protecting privacy while enabling efficient and accurate healthcare delivery. Patients can control their health records and share them with healthcare providers as needed.
Supply Chain Management
Blockchain digital identities enhance supply chain management by verifying the authenticity of products and preventing fraud. Each product can be assigned a digital identity, ensuring transparency and traceability throughout the supply chain.
Online Voting and Election Integrity
Blockchain-based digital identities can secure online voting systems by ensuring that each vote is cast by a verified, unique individual. This prevents fraud and enhances the integrity of the electoral process.
Enhancing Social Media Integrity
Blockchain digital identities can mitigate issues related to fake identities and Sybil attacks on social media platforms. By verifying user identities, platforms can enhance trust and reduce the spread of misinformation.
Real-World Examples in a Table
| Use Case | Description | Real-World Example |
| Banking and Finance | Streamlines identity verification, reducing fraud and enhancing customer experience through secure and automated KYC processes. | Jumio: Real-time identity verification using blockchain. |
| Government Services | Provides secure and tamper-proof digital identities for citizens, enabling streamlined and efficient access to government services. | Estonia’s e-Residency: Blockchain-based digital identity for e-residents. |
| Healthcare | Ensures secure access to patient data, protecting privacy while enabling efficient and accurate healthcare delivery. | Medicalchain: Blockchain-based electronic health record management. |
| Supply Chain Management | Enhances transparency and traceability by assigning digital identities to products, preventing fraud. | Everledger: Digital identities for diamonds and valuable goods. |
| Online Voting | Secures online voting systems by verifying voter identities, ensuring election integrity and preventing fraud. | Voatz: Blockchain-based online voting platform. |
| Social Media Integrity | Mitigates fake identities and Sybil attacks by verifying user identities, enhancing trust and reducing misinformation. | Civic: Identity verification platform for social media security. |
These examples illustrate the practical applications of blockchain digital identity across diverse sectors, highlighting the technology’s potential to revolutionize identity management and enhance security, privacy, and efficiency in various domains.
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI)
Self-Sovereign Identity (SSI) marks a significant shift in digital identity management, emphasizing user control and decentralization. SSI enables individuals to own, manage, and share their personal information independently, enhancing privacy, security, and autonomy.
The core principle of SSI is that individuals have full ownership and control over their personal data, in contrast to traditional systems where centralized entities manage identities. Key principles include:
- User Control and Ownership: Individuals create and manage their identities independently, deciding what information to share and with whom.
- Decentralization: SSI uses blockchain and other decentralized technologies to eliminate the need for central authorities, enhancing security.
- Privacy by Design: Users can share only necessary information without disclosing excessive personal details, ensuring privacy and data protection.
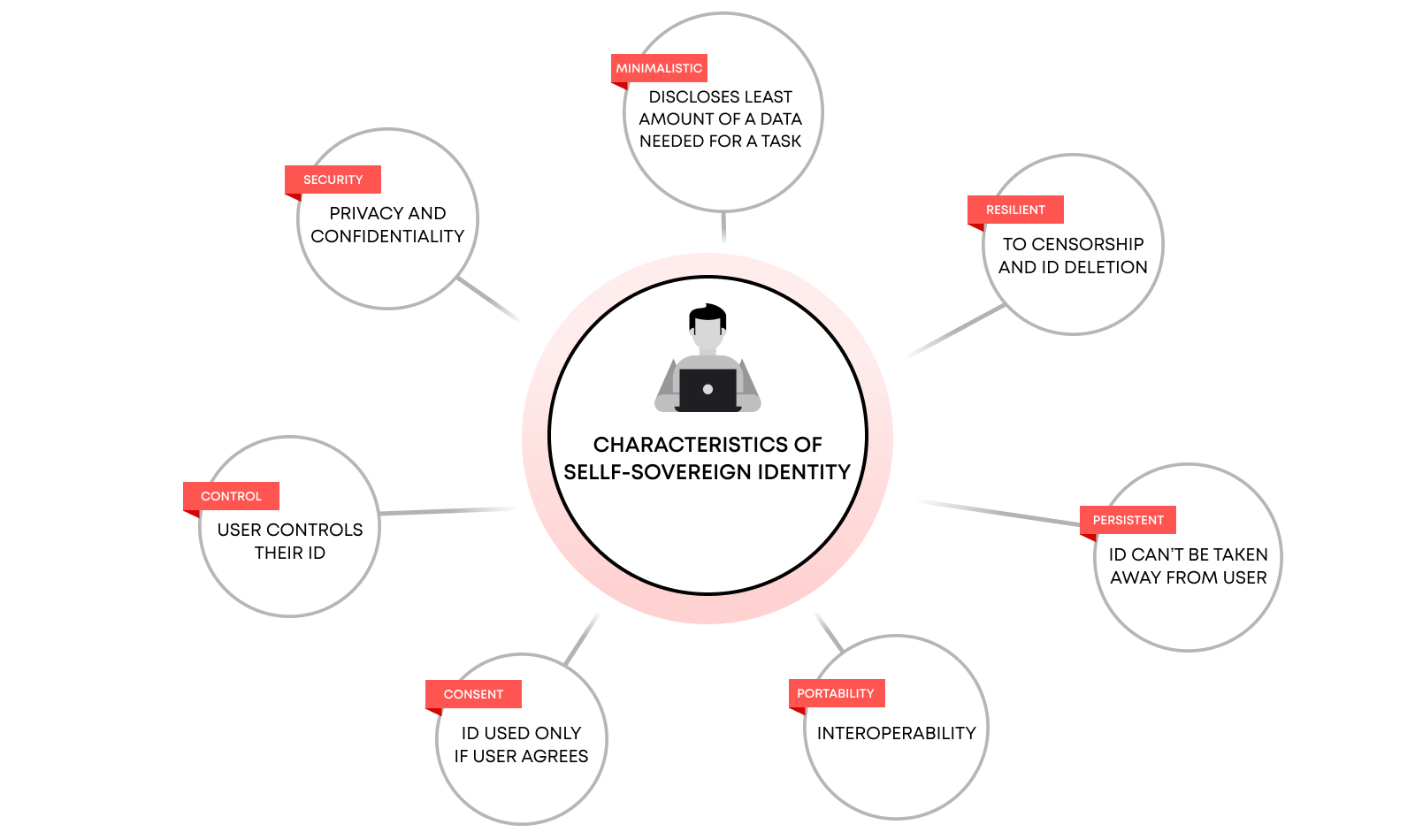
While still in early stages, SSI has the potential to revolutionize digital identity management. Key challenges include developing global standards, creating supportive regulatory frameworks, and educating users. Initiatives like the ID2020 Alliance and the Decentralized Identity Foundation are working to promote SSI adoption, aiming to make it the standard for digital identity management in the digital age.
Data Monetization and Portability
Blockchain-based digital identity systems not only enhance security and privacy but also open up new avenues for data monetization and portability. These features empower users to control and benefit from their personal data, aligning with regulatory requirements and market trends.
Data Monetization
One of the most transformative aspects of blockchain-based identities is the ability for users to monetize their personal data. Traditional data monetization models often exploit users by collecting and selling their data without explicit consent. Blockchain technology flips this model by enabling individuals to directly participate in the monetization process.
Data Portability
Data portability is another significant benefit of blockchain-based digital identities. It allows users to transfer their personal data seamlessly between different service providers without losing control or compromising privacy.
Practical Applications of the aforementioned principles include:
- Financial Services: Users can transfer their verified KYC data between different financial institutions, reducing redundancy and improving efficiency.
- Healthcare: Patients can move their medical records securely between healthcare providers, ensuring continuity of care and avoiding the need for repeated tests and procedures.
- Employment: Job seekers can share their verified credentials and employment history with potential employers across different job platforms, simplifying the hiring process.
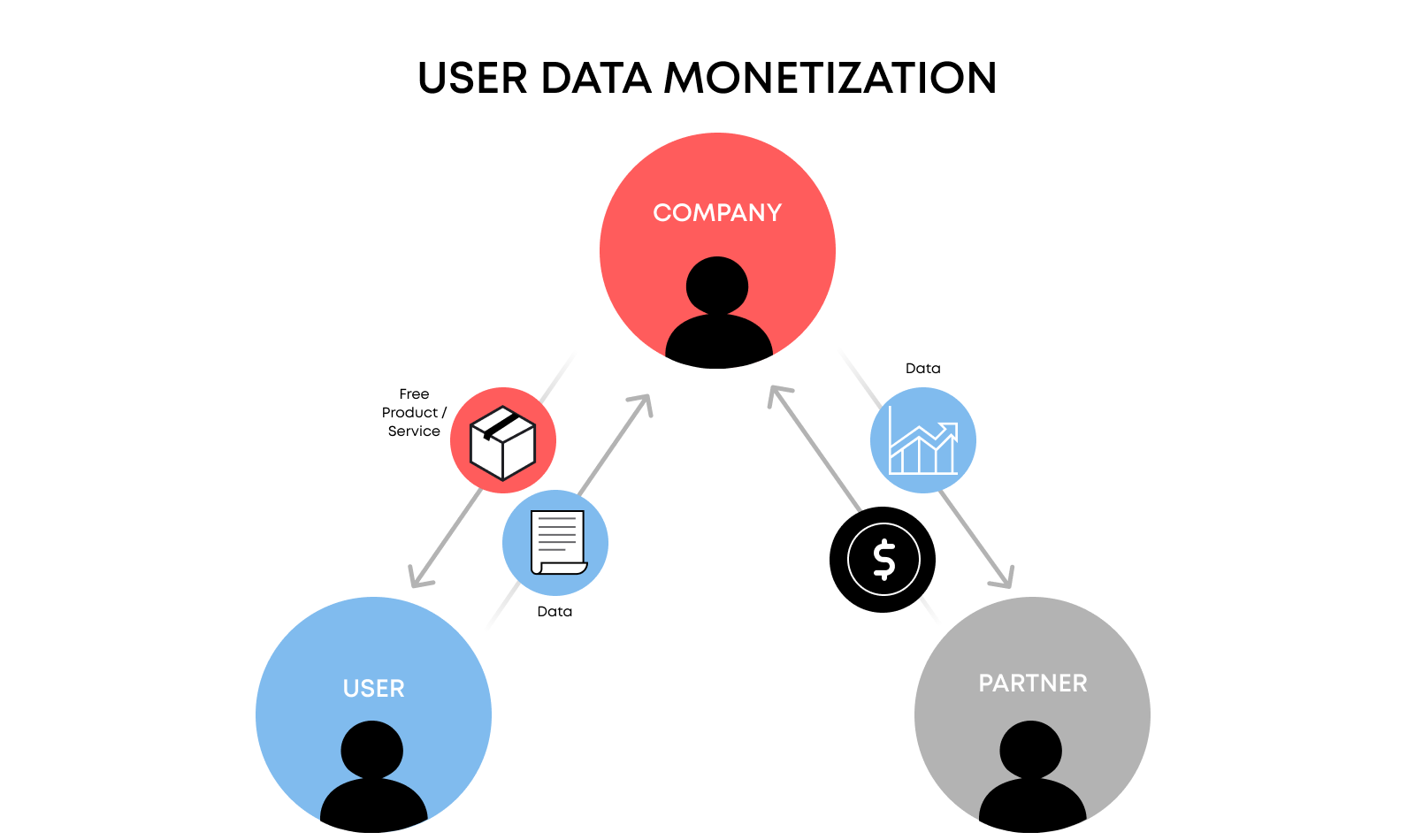
Blockchain-based digital identity systems provide robust mechanisms for data monetization and portability, empowering users with control over their personal information. These features not only enhance user privacy and security but also create new opportunities for economic participation and regulatory compliance. As the digital economy continues to evolve, the ability to monetize and port data will become increasingly valuable, making blockchain-based identities a critical component of future digital interactions.
Challenges and Future of Digital Identity Blockchain
Despite the potential benefits, several challenges hinder the widespread adoption of blockchain-based digital identities:
- Technological hurdles: Scalability, interoperability, and user experience need to be improved.
- Regulatory challenges: Legal frameworks must adapt to accommodate decentralized identity systems.
Future developments in this field include ongoing research and initiatives like the ID2020 Alliance, which aims to promote and standardize digital identity solutions globally. As technology and regulations evolve, blockchain identity management is expected to play a critical role in shaping the future of digital identity.
By leveraging the strengths of blockchain technology, digital identity systems can become more secure, private, and user-centric, offering significant benefits across various sectors and paving the way for a more reliable digital economy.
