Cross-Chain Interoperability: Unlocking the Power of Blockchain
Despite the great potential of blockchain, the technology faces a fundamental challenge: solitary ecosystems. Each blockchain operates in isolation, bound by its unique protocols, consensus mechanisms, and governance models, thus impeding seamless interaction. This fragmentation hinders the fluid exchange of information and value across different blockchain networks, presenting a significant barrier to the technology’s vision of creating a decentralized, interconnected digital world.
The question of why two blockchains cannot inherently interact with each other stems from their foundational design. Blockchains are built as independent ledgers, each with its distinct governance rules, security protocols, and data structures. This autonomy ensures security and integrity within each network but also creates an environment where interoperability is not natively built-in. Traditional financial systems, in contrast, have developed standardized protocols over decades that facilitate interbank communication.
In the blockchain world, however, the absence of a universal standard for cross-chain communication necessitates the development of interoperability solutions. Cross-chain interoperability thus serves as the bridge, enabling diverse blockchain networks to overcome their inherent isolation and participate in a more integrated, expansive digital economy.
For a deeper understanding of how blockchain networks can be connected, explore Blaize comprehensive article on blockchain bridges.
Cross-chain interoperability, then, becomes the critical solution. It represents the technological capability that enables disparate blockchain networks to communicate, share resources, and transfer value. This breakthrough overcomes the inherent limitations posed by isolated blockchains and amplifies the utility, efficiency, and scalability of blockchain applications. By bridging these divides, cross-chain interoperability fosters an ecosystem where information and assets flow freely, unlocking new opportunities for collaboration and innovation.
Why is Cross-Chain Interoperability so Important?
Cross-chain interoperability is not just a technical achievement but a vital component for the future scalability, versatility, and adoption of blockchain technologies. This interconnectedness allows for the creation of sophisticated, decentralized applications that can leverage the unique strengths of multiple blockchain platforms, thereby enhancing user experience, efficiency, and utility.
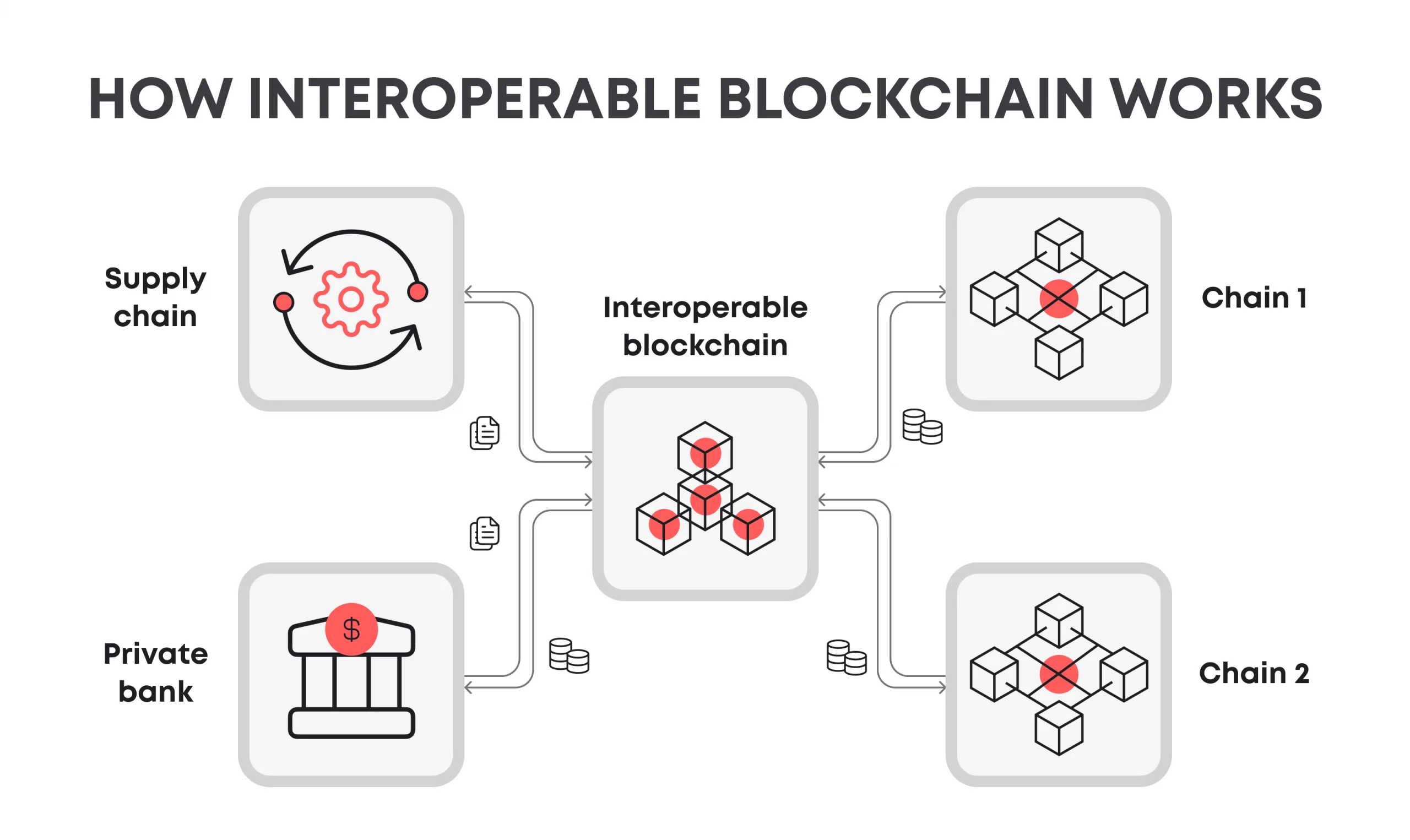
The significance of cross-chain interoperability extends beyond mere asset transfer. It is foundational for achieving a truly decentralized and collaborative digital ecosystem. By enabling blockchains to interact without intermediaries, it fosters an environment where innovation can flourish, unhampered by the technological and philosophical divides that currently segment the blockchain space. This cross-communication capability ensures that blockchain technology can move towards a future where financial systems, supply chains, and digital identities are interconnected, providing a level of interoperability that matches, or even surpasses, that of current centralized systems.
Moreover, interoperability addresses one of the blockchain industry’s pressing challenges: network silos. It does so by enabling a fluid exchange of value and data across different blockchain networks, which, in turn, can lead to an increase in liquidity, improved security protocols through shared intelligence, and the creation of new markets and business models that were previously inconceivable. Projects and platforms that embrace cross-chain technology are at the forefront, driving the industry towards a more integrated, efficient, and user-centric future.
This is the vision that cross-chain interoperability promises, and its importance lies in several key areas:
| Benefit: | Description: | Example: |
| Enhanced DeFi Experience | Currently, DeFi applications are largely restricted to the blockchain they’re built on. Cross-chain interoperability allows users to access a wider range of DeFi protocols and services, regardless of the underlying blockchain. Imagine seamlessly transferring your funds from a high-yield savings protocol on Ethereum to a lending platform on Solana for better interest rates. | Cross-chain interoperability protocols (CCIPs) like CCIP crypto: CCIP Explorer facilitate secure cross-chain communication, enabling innovative DeFi applications that leverage the strengths of multiple blockchains. |
| Increased Liquidity | Fragmented liquidity across different blockchains hinders overall market efficiency. Cross-chain bridges allow assets to flow freely between blockchains, creating a more unified and liquid cryptocurrency market. This benefits both users (easier access to assets) and projects (deeper liquidity pools). | Eigen Layer facilitates interoperability and secure asset transfers across various blockchain networks. By leveraging technologies like Eigen Layer, the blockchain ecosystem can achieve enhanced liquidity, allowing for smoother transactions and greater access to diverse assets for participants across the board. |
| Innovation and Interconnectedness | Cross-chain interoperability fosters a more interconnected blockchain ecosystem. Developers can leverage the unique features of different blockchains to build innovative applications. Imagine a supply chain management platform that utilizes the security of Bitcoin for record-keeping and the scalability of Ethereum for real-time tracking. | Wormhole, a leading cross-chain protocol, significantly enhances blockchain interoperability by enabling asset and information exchange across diverse networks. |
| Improved User Experience | Currently, using different blockchains can be cumbersome, requiring users to manage multiple wallets and navigate complex interfaces. Cross-chain interoperability removes these barriers, creating a more seamless and user-friendly experience. | Cross-chain messaging protocols like Axelar Network allow developers to build applications that can interact with assets and data on different blockchains without requiring users to manage complex infrastructure. |
What are Blockchain Interoperability Solutions?
Imagine a world where different blockchains, each with their own strengths and functionalities, could seamlessly exchange information and assets. This interconnected future is what cross-chain interoperability promises to deliver. But how exactly do we achieve this communication between isolated blockchains? Let’s delve into the various solutions that are breaking down these barriers.
Cross-Chain Bridges
Cross-chain bridges act as intermediaries between blockchains, facilitating the secure transfer of assets and data. These bridges typically lock assets on the originating chain and mint an equivalent representation on the destination chain. When the user wants to return the asset, the bridge burns the representation on the destination chain and unlocks the original asset on the originating chain.
Examples:
- Wormhole: Wormhole is a generic cross-chain bridge protocol that facilitates asset transfers between various blockchains like Ethereum, Solana, and Avalanche.
- Multichain (formerly AnySwap): Multichain is a popular cross-chain bridge solution supporting a wide range of blockchains, known for its user-friendly interface and fast transaction times.
Read Also: Blaize comprehensive guide on how to launch a dApp, bridge and parachain on Polkadot.
Shared Validators
Shared validator protocols leverage a set of validators who participate in securing both blockchains. These validators are responsible for verifying transactions on both chains, creating a trustless environment for communication and data exchange.
Pros:
- More efficient than traditional bridges: Shared validator protocols can be more efficient than traditional cross-chain bridges as they don’t require locking assets.
- Potentially lower fees: Transactions involving shared validator protocols may incur lower fees compared to bridge transactions.
Cons:
- Requires coordination between blockchains: Implementing shared validator protocols requires a high degree of coordination between the participating blockchains.
- May not be suitable for all types of communication: Shared validator protocols might not be ideal for all types of cross-chain communication, particularly for complex data transfers.
Examples:
- Cosmos Hub: connects several subchains via Cosmos IBC (Inter-Blockchain Communication). IBC can leverage shared validator sets between Cosmos-based blockchains to facilitate secure and efficient communication.
- Polkadot parachains: Polkadot utilizes a shared security model where validators securing the main relay chain (Polkadot) can also participate in securing parachains (application-specific blockchains) connected to the relay chain.
Light Clients & Oracles
Light client protocols and oracles form a powerful duo for achieving blockchain interoperability. These light clients reside on another blockchain and can efficiently communicate with the main chain. Think of oracles as information bridges. They act as trusted intermediaries, retrieving data from the source blockchain (where the light client resides) and relaying it to the target blockchain. This allows the target blockchain to verify the information without needing to download the entire history of the source chain.
Pros:
- Efficient and Scalable: Light clients are compact and require minimal resources, making them ideal for frequent data transfers. This scalability is particularly beneficial for applications requiring real-time data feeds from multiple blockchains.
- No Locked Assets: Unlike bridge solutions, light clients don’t require users to lock up their assets on a separate platform. This eliminates the risk of centralization associated with bridges.
Cons:
- Relies on the Trust of Oracles: The security of the entire system hinges on the reliability of oracles. Malicious or compromised oracles could potentially feed false information into the network.
- Potential Data Manipulation Risks: Since oracles act as intermediaries, there’s a possibility of data manipulation if they’re not carefully designed and implemented.
Examples:
- Chainlink: A prominent decentralized oracle network (DON) that provides secure and reliable data feeds for various blockchain applications.
- Pyth Network: A decentralized oracle network that provides a wide array of data types on-chain through Pyth Oracles, featuring advanced verification mechanisms to ensure the accuracy and reliability of data.
Layer 2 Scaling Solutions
Layer 2 scaling solutions operate on top of a main chain, inheriting security from the main chain while enabling faster transactions. Some Layer 2 solutions, like rollups and Validium, are incorporating interoperability features to allow communication and asset transfer between the Layer 2 network and the main chain, or even other Layer 2 solutions.
Pros:
- Faster transactions compared to main chain: Layer 2 solutions offer significantly faster and cheaper transactions compared to the main chain.
- Potential for interoperability with other Layer 2 solutions: Interoperable Layer 2 solutions can create a more interconnected ecosystem with seamless asset and data flow.
Cons:
- Complexity for developers: Developing applications for interoperable Layer 2 solutions can be more complex compared to traditional blockchain development.
- May not be suitable for all types of applications: Not all applications may benefit from the specific features offered by interoperable Layer 2 solutions.
Examples:
- Optimism (Layer 2 for Ethereum): Optimism is a Layer 2 rollup solution for Ethereum that is exploring interoperability features to enable communication with other blockchains.
- Avalanche: A highly scalable blockchain platform that utilizes subnets as Layer 2 solutions to enhance its own network, focusing on interoperability to seamlessly connect with other networks and subnets, fostering a unified and efficient ecosystem.
Emerging Solutions: LayerZero & Axelar
LayerZero and Axelar represent innovative approaches to blockchain interoperability. These solutions utilize concepts like “stateless communication” and “secure relays” to facilitate fast and secure cross-chain communication.
Pros:
- Promise high security and fast communication: These emerging solutions aim to address scalability and security limitations of existing interoperability solutions.
- Innovative solutions for the future of interoperability: LayerZero and Axelar represent promising advancements in cross-chain communication technology.
Cons:
- Still under development: These solutions are still under development and require further testing and adoption before widespread use.
- Limited adoption compared to established solutions: Currently, LayerZero and Axelar have a smaller user base compared to more established interoperability solutions.
Examples:
- LayerZero: LayerZero is a promising interoperability protocol that utilizes “stateless communication” for secure and efficient cross-chain interaction.
- Axelar: Axelar is another emerging solution that leverages “secure relays” to facilitate fast and reliable cross-chain communication.
| Solution | Brief Description | Pros | Cons |
| Cross-Chain Bridges | Separate blockchain facilitates asset and data transfer. | Enables communication between dissimilar blockchains, high security. | Centralization risks, potential delays and fees. |
| Shared Validators | Validators secure both blockchains, enabling trustless communication. | More efficient than bridges, potentially lower fees. | Requires coordination between blockchains, may not be suitable for all communication. |
| Light Clients & Oracles | Lightweight clients verify data from another chain relayed by oracles. | Efficient and scalable, no locked assets. | Relies on trust of oracles, potential data manipulation risks. |
| Layer 2 Solutions (with interoperability) | Layer 2 solutions on top of a main chain with interoperability features. | Faster transactions, potential interoperability with other Layer 2s. | Complexity for developers, may not suit all applications. |
| LayerZero & Axelar (Emerging Solutions) | Utilize novel approaches for secure and fast communication. | Promise high security and fast communication, innovative solutions. | Still under development, limited adoption. |
By understanding the different approaches to blockchain interoperability, developers and users can choose the most suitable solution for their specific needs. As the field continues to evolve, we can expect even more innovative solutions to emerge, paving the way for a truly interconnected blockchain future.
Blaize Expertise
Now that we’ve explored the various approaches to achieving cross-chain interoperability, let’s delve into Blaize’s expertise in this domain. As a leading blockchain development agency, Blaize possesses a deep understanding of bridge technology, a cornerstone solution for enabling communication and asset transfer between blockchains. We’ll showcase how Blaize leverages its bridge expertise to craft secure and efficient cross-chain solutions, empowering businesses to unlock the full potential of blockchain interoperability.
1.Smart Contract Security Audit for Rainbow Bridge by Aurora

Overview: Blaize was approached by Aurora for a comprehensive security audit of their Rainbow Bridge, a vital component facilitating asset transfers between NEAR and Ethereum blockchains. This project’s complexity demanded a meticulous approach to ensure the robustness and security of the bridge.
Challenge: The task was to scrutinize the smart contracts relayers and other additional services of Rainbow Bridge for potential vulnerabilities. So the main challenge was in multi-components. Given the bridge’s critical role in asset transfer, any security lapse could lead to significant financial and reputational damage. As well, within this project a combined team of experts from Blaize and Aurora was involved.
Solution: Blaize’s team of expert auditors conducted a thorough analysis of the smart contracts. They employed advanced tools and techniques to identify and address security vulnerabilities, ensuring compliance with best practices in blockchain security.
Outcome: The audit was successful, leading to the enhancement of the Rainbow Bridge’s security architecture. Blaize’s intervention fortified the bridge against potential attacks, instilling confidence in its users and stakeholders.
Read more about Rainbow Bridge case by Blaize here.
2.Smart Contract Security Audit for BlueLight Kale Bridge

Overview: BlueLight sought Blaize’s expertise for a security audit of their Kale Bridge, a blockchain bridge designed to enable seamless asset transfers across multiple blockchains.
Challenge: The major hurdle was to ensure the impenetrability of the Kale Bridge against a wide array of threats. The bridge’s modular functionality and integration with various blockchains amplified the need for a comprehensive security strategy.
Solution: Blaize deployed its seasoned team to conduct an exhaustive audit of the bridge’s smart contracts. The team’s complex multi-step auditing strategy with cross-verifications between auditors to uncover any security flaws, ensuring the bridge operated with the highest security standards.
Outcome: The thorough audit resulted in the identification and rectification of several critical security issues. Blaize’s contribution significantly elevated the security profile of the Kale Bridge, making it a reliable and secure platform for asset transfers.
Read more about BlueLight Kale Bridge case by Blaize here.
3.Atomic Swap Bridge Development for REMME Chain

Overview: REMME Chain engaged Blaize to develop an atomic swap bridge, a decentralized solution for exchanging assets across different blockchains without intermediaries.
Challenge: The task was challenging due to the technical complexity involved in creating a decentralized, trustless system for asset exchange. The bridge needed to be efficient, secure, and user-friendly to gain widespread adoption.
Solution: Blaize took on this challenge by leveraging its deep expertise in blockchain technology. The team developed a robust atomic swap bridge with an intuitive interface, ensuring seamless and secure transactions across blockchains.
Outcome: The successful development of the atomic swap bridge for REMME Chain marked a significant milestone. It enabled users to conduct cross-chain transactions securely and efficiently, enhancing the utility and reach of the REMME ecosystem.
Read more about REMME Chain by Blaize here.
Limitations, Challenges and Risks of Blockchain Interoperability
While blockchain interoperability opens up a world of possibilities by connecting disparate blockchain ecosystems, it also brings to the fore a range of technical, security, scalability, governance, and dependence challenges. Addressing these issues requires a concerted effort from the blockchain community to develop interoperability solutions that are not only technically sound and secure but also scalable, standardized, and able to operate within a decentralized governance framework.
Limitations:
- Blockchain Heterogeneity: Blockchains, much like biological organisms, exhibit a remarkable degree of heterogeneity. Divergences in architectural design, consensus mechanisms, and security paradigms present a significant challenge in fostering seamless interoperability.
- Scalability Bottlenecks: Current interoperability solutions can introduce additional processing burdens, potentially hindering the overall scalability of the blockchain landscape. Striking a balance between facilitating cross-chain communication and maintaining efficient transaction throughput remains a critical objective.
Challenges:
- Security Vulnerabilities: Bridging the divide between blockchains inherently creates new attack vectors. Security weaknesses in any component of the interoperability stack, encompassing bridges and oracles, can have cascading ramifications across the entire ecosystem. Robust security measures are paramount in ensuring the integrity and resilience of cross-chain interactions.
- Standardization Hurdles: The absence of universally adopted standards for cross-chain communication fragments the ecosystem and impedes smooth interoperability. A plethora of competing protocols and approaches create compatibility roadblocks and limit the potential for network effects. Establishing industry-wide standards is crucial for fostering a cohesive and interoperable blockchain future.
- User Experience Friction: Existing interoperability solutions can often be cumbersome for users, demanding navigation of complex interfaces and management of multiple wallets across disparate blockchains. Simplifying the user experience and fostering intuitive interaction paradigms are critical for achieving widespread adoption.
Risks:
- Centralization Pitfalls: Many interoperability solutions exhibit a reliance on centralized entities, such as bridge operators or oracles. This introduces a single point of failure and potentially undermines the core tenets of decentralization that underpin blockchain technology. Mitigating centralization risks through innovative solutions that prioritize distributed control is essential.
- Data Integrity Concerns: The accuracy and reliability of data relayed between blockchains is paramount. Malicious actors or systemic malfunctions could potentially lead to the transmission of inaccurate or manipulated data, disrupting applications and causing financial losses. Ensuring the veracity and integrity of cross-chain data exchanges is critical for fostering trust and promoting the secure utilization of interoperable functionalities.
While the challenges and risks associated with cross-chain interoperability are undeniable, the potential benefits of a truly interconnected blockchain landscape are equally compelling. As the field continues to mature, we can anticipate advancements in interoperability protocols that address these limitations and mitigate the associated risks. The development of secure, scalable, and user-centric solutions is paramount for unlocking the full potential of blockchain technology and ushering in a new era of collaborative innovation.
Final Thoughts on Cross Chain Interoperability
The significance of interoperability cannot be overstated – it is the key that unlocks the full potential of blockchain technology, enabling diverse networks to communicate and collaborate seamlessly. This integration fosters plenty of opportunities for innovation, efficiency, and growth across various sectors, from finance to healthcare, and beyond.
However, as we venture into this domain, it is imperative to approach the challenges of interoperability with a keen sense of caution and responsibility. The path towards a fully interoperable blockchain ecosystem is fraught with technical complexities, security risks, and governance issues. It demands not only technological prowess but also a collaborative spirit among stakeholders across the blockchain domain.
In this domain, the role of companies like Blaize, having extensive expertise in multiple blockchain ecosystems is invaluable. By dealing with the multifaceted challenges of cross-chain communication, such initiatives are paving the way for a more inclusive, efficient, and innovative blockchain future.
In conclusion, cross-chain interoperability is not merely a feature of the blockchain landscape but a cornerstone upon which the future of decentralized technology will be built. Its successful implementation will craft a new age of digital collaboration, bringing to fruition the promise of blockchain technology in creating a more open, efficient, and interconnected world.
FAQ
What is blockchain interoperability?
Blockchain interoperability is the capability of different blockchain platforms to communicate, exchange information, and transfer assets across their networks without hindrances. This feature is vital for creating a cohesive digital ecosystem, where diverse blockchains can work together harmoniously, enhancing the overall functionality and value of the blockchain space. Interoperability addresses the challenge of blockchain isolation, enabling a more integrated, efficient, and user-friendly experience across various blockchain applications.
What is cross-chain technology?
Cross-chain technology refers to a set of techniques and protocols developed to facilitate blockchain interoperability, allowing independent blockchain networks to interact and share information and assets seamlessly. This technology plays a critical role in overcoming the limitations of single, isolated blockchain systems, paving the way for innovative cross-chain applications and services. By leveraging cross-chain technology, developers and users can unlock new possibilities for collaboration and value exchange in the decentralized world.
How does blockchain interoperability work?
Blockchain interoperability functions through the implementation of various technological solutions such as blockchain bridges, sidechains, and specific interoperability protocols. These tools and frameworks enable secure and efficient communication and asset transfers between distinct blockchain networks. By establishing a standard protocol or creating a bridge that connects two blockchains, interoperability solutions ensure that transactions and information can flow freely and reliably across the blockchain ecosystem, fostering greater collaboration and innovation.
Why is blockchain interoperability important?
Blockchain interoperability is crucial for enhancing the scalability, efficiency, and usability of blockchain technology, ensuring its wider adoption and practical application in numerous industries. It allows for a more connected blockchain ecosystem, where different networks can leverage each other’s strengths, share resources, and create more complex, versatile applications. Moreover, interoperability facilitates a smoother user experience, enabling users to interact with multiple blockchain platforms without needing to manage multiple wallets or navigate through complex conversion processes.
How is blockchain interoperability achieved?
Achieving blockchain interoperability involves the strategic deployment of bridges, sidechains, layer 2 solutions, and dedicated interoperability protocols. These solutions provide the necessary infrastructure for different blockchains to communicate and share assets securely and efficiently. By adopting standards and frameworks that support interoperability, blockchain developers and organizations can create an interconnected network of blockchains, enhancing the overall potential and impact of blockchain technology in solving real-world problems.
Contact Blaize to get first-class bridges development services.
