What Stands for Mysterious DeSo: The Power of Decentralized Social Media
In today’s digital landscape, decentralized social media networks are emerging as a groundbreaking innovation that challenges the traditional model of online interaction. These networks utilize blockchain technology to distribute control among users rather than centralizing it in a single entity.

The potential and prospectiveness of decentralized social media are underscored by significant academic and industry interest. The MIT Center for Civic Media, through its DeSoc initiative, explores the transformative power of decentralized social networks. This initiative highlights the importance of decentralization in creating more equitable, inclusive, and resilient digital communities.
The market for decentralized social networks is projected to grow significantly in the coming years. The global decentralized social network market is expected to reach a valuation of USD 101.2 billion by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 23.6% from 2023 to 2033. This rapid growth is driven by increasing user awareness and the demand for greater control over personal data and content. The United States and East Asia, particularly China and Japan, are anticipated to be key markets, with high growth rates expected in these regions.
Despite their potential, decentralized social media networks face significant challenges in gaining widespread popularity. Statistics show that decentralized platforms currently account for less than 1% of the total social media user base.
One of the main issues is that the concept of decentralization is not a compelling selling point for the average user. Most people do not prioritize decentralization or privacy enough to switch from well-established platforms like Facebook or Twitter. These networks often lack engaging content and user participation, making them less attractive to potential users.
Additionally, the incentive structures for companies operating these networks are not aligned with long-term growth, as user data ownership allows easy migration between platforms. Early adopters of decentralized social networks are typically from the crypto ecosystem, driven more by financial incentives than by the desire to build a sustainable community. Furthermore, the complexity of blockchain technology and the necessity to manage private keys and wallets can pose significant barriers to mass adoption.
However, the key to driving the adoption of decentralized social media lies in creating a superior product. Blaize excels in developing user-friendly, secure, and innovative web3 solutions that can address these challenges. By focusing on enhancing user experience and functionality, decentralized social networks have the potential to attract a broader audience and revolutionize digital interaction.
How Decentralized Social Media Networks Work
Decentralized social media networks operate on the foundational principles of blockchain technology and smart contracts, creating a robust, secure, and user-centric ecosystem. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the components that make decentralized social media networks function effectively:
1. Blockchain Technology
Role and Function: Blockchain serves as the underlying infrastructure for decentralized social networks. It is a distributed ledger technology that records transactions across multiple computers, ensuring data integrity and security.
- Transparency and Security: Blockchain ensures that all transactions and data changes are transparent and immutable. Each block contains a cryptographic hash of the previous block, a timestamp, and transaction data, making it tamper-proof.
- Decentralization: Instead of a central authority, blockchain relies on a network of nodes (computers) to validate and record transactions. This decentralization prevents a single point of failure and reduces the risk of data breaches.
2. Smart Contracts
Role and Function: Smart contracts are self-executing contracts with the terms of the agreement directly written into code. They automatically enforce and execute transactions when predefined conditions are met.
- Automation and Efficiency: Smart contracts automate various processes, such as content monetization, user interactions, and governance. This reduces the need for intermediaries and enhances operational efficiency.
- Trustless Environment: Smart contracts operate in a trustless environment, meaning transactions are executed based on code without requiring trust between parties. This is crucial for maintaining fairness and transparency.
3. Peer-to-Peer Network Structure
Role and Function: The peer-to-peer (P2P) network structure distributes data across multiple nodes, ensuring redundancy and availability.
- Data Distribution: In a P2P network, data is not stored in a central server but distributed across various nodes. This enhances data availability and reduces the risk of data loss.
- Node Functionality: Each node in the network participates in data storage and verification processes. Nodes can be run by users, who contribute to the network’s security and efficiency.
4. Decentralized Storage Solutions
Role and Function: Decentralized storage solutions like the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) play a critical role in storing and retrieving data in a decentralized manner.
- Data Redundancy: IPFS breaks files into smaller pieces, distributes them across multiple nodes, and assigns unique identifiers (hashes) to each piece. This ensures data redundancy and quick retrieval.
- Content Addressing: Unlike traditional URL-based addressing, IPFS uses content addressing, where data is retrieved based on its unique hash rather than its location. This enhances security and accessibility.
5. Governance Models
Role and Function: Decentralized social networks often employ decentralized governance models, allowing users to participate in decision-making processes.
- Token-Based Voting: Users holding the network’s tokens can vote on proposals regarding platform development, feature implementation, and policy changes.
- Community Governance: Governance structures vary but often involve community-driven decision-making, ensuring that the platform evolves according to the collective interests of its users.
By integrating these components, decentralized social media networks create a secure, transparent, and user-focused ecosystem. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring the network’s functionality, security, and resilience, paving the way for a more equitable digital interaction environment.
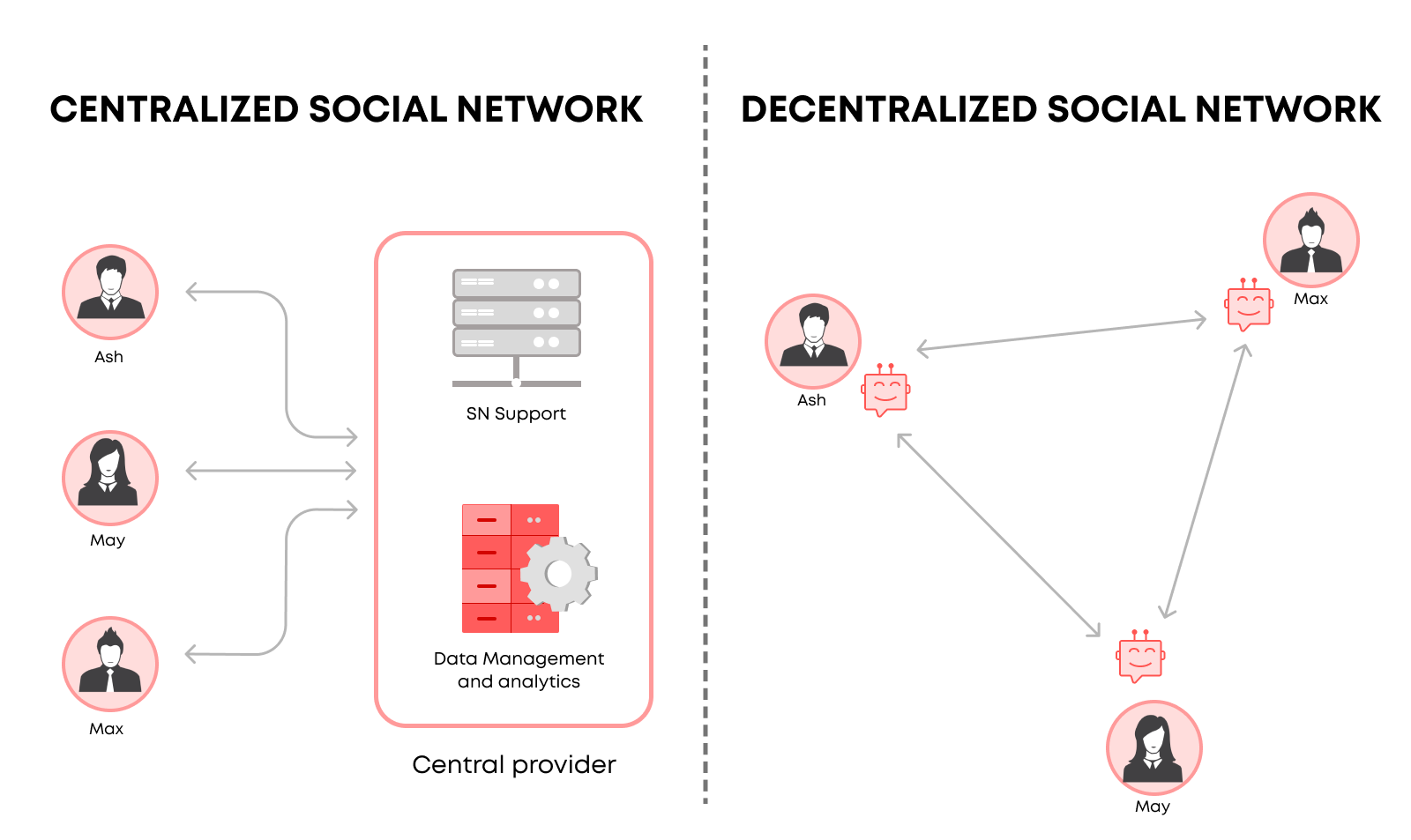
Centralized vs Decentralized Social Networks
Centralized and decentralized social networks represent two fundamentally different approaches to online interaction, each with its own set of characteristics, advantages, and drawbacks. Understanding these differences is crucial for grasping the potential of decentralized social media and its implications for the future of digital communication.

Centralized Social Networks
Definition: Centralized social networks are platforms where a single entity (such as a company) controls the entire network. This entity manages user data, content moderation, and platform policies.
- Data Control: In centralized networks, the platform owner has full control over user data. This often leads to data privacy concerns, as user information can be accessed, monetized, or shared without explicit consent.
- Censorship: Centralized platforms can impose content restrictions and censorship based on their policies, which might align with regulatory requirements or the platform’s own guidelines.
- Monetization: The platform typically monetizes through advertising, data sales, and other revenue streams. Users have limited opportunities to earn directly from their content.
- User Autonomy: Users have limited control over their content and interactions. Changes in platform policies or algorithms can significantly impact user experience.
- Scalability and Performance: Centralized networks can scale efficiently, providing smooth user experiences due to their robust infrastructure and resources.
Decentralized Social Networks
Definition: Decentralized social networks operate on blockchain technology, distributing control across a network of nodes rather than centralizing it in a single entity.
- Data Control: Users retain ownership of their data. Information is stored across a decentralized network, reducing the risk of unauthorized access and data breaches.
- Censorship Resistance: Decentralized networks are less prone to censorship. Content moderation is often community-driven, ensuring freedom of expression.
- Monetization: Decentralized platforms offer more equitable monetization models. Users can earn directly through mechanisms like crypto tokens, tipping, or other blockchain-based rewards.
- User Autonomy: Users have greater control over their content and interactions. They can migrate their data and identity across platforms without losing their social network.
- Scalability and Performance: Decentralized networks face scalability challenges. The distributed nature can lead to slower performance and higher latency compared to centralized counterparts.
| Feature | Centralized Social Networks | Decentralized Social Networks |
| Data Control | Controlled by platform owners | Retained by users |
| Censorship | Platform-imposed | Community-driven, less prone to censorship |
| Monetization | Platform-centric (ads, data sales) | User-centric (crypto tokens, direct rewards) |
| User Autonomy | Limited | High |
| Scalability | High (efficient infrastructure) | Challenging (distributed nature) |
| Privacy | Moderate to low | High |
| Security | Centralized security measures | Decentralized, blockchain-based security |
| Governance | Centralized (platform policies) | Decentralized (community voting, token-based governance) |
| Content Moderation | Platform-enforced | Community-enforced |
| Innovation | Depends on the platform’s vision and resources | Driven by open-source community and decentralized initiatives |
Centralized social networks excel in scalability and performance, providing seamless user experiences thanks to their robust infrastructures. However, they often fall short in areas of data privacy, user control, and censorship resistance. On the other hand, decentralized social networks offer enhanced privacy, user autonomy, and censorship resistance, but face significant challenges in scalability and user adoption due to their complex underlying technologies.
The future of digital interaction may lie in finding a balance between these two models, leveraging the strengths of both centralized efficiency and decentralized user empowerment. By focusing on improving user experience and addressing scalability issues, decentralized social networks can become viable alternatives to traditional platforms, potentially revolutionizing how we interact online.
Key Features and Advantages of Decentralized Social Media
Decentralized social media networks are transforming the way we interact online by offering unique features and benefits that address many of the shortcomings associated with traditional, centralized platforms. Here’s an in-depth look at the key features and advantages of decentralized social media:
Enhanced Control Over Content
Decentralized social media networks provide users with unparalleled control over their content, a significant departure from traditional platforms. This control stems from the immutable nature of blockchain technology, which ensures that content ownership is verifiable and tamper-proof.
- Content Ownership: On decentralized social networks, content is recorded on the blockchain, providing irrefutable proof of ownership. Unlike centralized platforms that store data on proprietary servers, the blockchain stamps each piece of content as belonging to the user. This decentralized ledger guarantees that ownership records cannot be falsified or manipulated, ensuring that users have permanent and unquestionable control over their personal information.
- Digital Signatures: Each piece of content on a decentralized network is accompanied by a digital signature. This cryptographic technique ensures the authenticity and integrity of the content, verifying that it was created and posted by the rightful owner. The digital signature helps protect against unauthorized alterations and reinforces the user’s control over their data.
Censorship Resistance
Decentralized networks are less vulnerable to censorship due to their distributed nature.
- Freedom of Expression: Without a central authority to impose content restrictions, users can share their views more freely. Content moderation is typically community-driven, ensuring a more democratic approach to what is allowed on the platform.
- Immutable Records: Once data is recorded on the blockchain, it cannot be altered or deleted, preserving the integrity of the information shared.
User Autonomy
Users have greater control over their interactions and content.
- Self-Governance: Users can make decisions regarding platform rules and policies through decentralized governance models, such as token-based voting.
- Interoperability: Decentralized identities allow users to move their data and social graphs across different platforms seamlessly, enhancing the continuity of their online presence.
Equitable Monetization
Decentralized platforms offer fairer revenue-sharing models that benefit content creators directly.
- Direct Earnings: Users can monetize their content through blockchain-based mechanisms like crypto tokens, tipping, and microtransactions without relying on advertising revenue controlled by the platform.
- Token Rewards: Users are often rewarded with tokens for their contributions, which can be traded or used within the network.
Interoperability and Integration
Decentralized social networks can integrate with various blockchain-based services to enhance functionality.
- Enhanced Functionality: Features such as decentralized storage, smart contracts, and crypto wallets and features from different blockchain networks can be integrated into social media platforms to offer unique functionalities not available on centralized networks.
- NFTs: NFTs can be used as social network accounts. For instance, platforms like Lens Protocol use NFTs to represent user profiles, allowing for unique, verifiable identities and the ability to transfer social media accounts between platforms. This enhances user control and ownership of their digital identity and content.
Enhanced Advertising Control and Friendliness
Decentralized networks offer higher controllability and friendliness of advertising, tokenizing attention to benefit both users and advertisers.
- User Choice: Users can choose what types of ads they want to see, enhancing their experience and reducing ad fatigue.
- Targeted Advertising: Advertisers benefit from more precise targeting based on user preferences and behaviors, leading to more effective ad campaigns.
- Tokenized Attention: Users can earn tokens for viewing ads, creating a more engaging and rewarding advertising ecosystem.
- Integration with Marketplaces: Decentralized social networks can seamlessly integrate with various marketplaces, allowing users to buy and sell goods and services directly through the platform. This integration enhances user engagement and provides new revenue streams for both users and advertisers.
Popular Decentralized Social Media Platforms
Decentralized social media platforms are gaining traction as alternatives to traditional, centralized networks. Each platform offers unique features, fostering diverse user communities and experiences. Below, we explore some of the most notable decentralized social media platforms, providing detailed descriptions and real-life examples of their functionalities and user bases.
Lens Protocol
Lens Protocol is one of the most popular and hyped decentralized social media platforms, offering unique features that leverage blockchain technology for social interactions.
- Features: Lens allows users to create profiles, follow others, and engage with content. It uniquely uses NFTs to represent user profiles, enabling verifiable identities and the ability to transfer social media accounts between platforms.
- User Base: Lens has rapidly gained popularity, particularly among blockchain enthusiasts and those interested in digital identity solutions.
- Real-Life Example: Users on Lens can seamlessly interact with each other, knowing that their profiles and content ownership are securely recorded on the blockchain.
Steemit
Steemit is a social media platform built on the STEEM blockchain that rewards users with cryptocurrency for creating and curating content.
- Features: Steemit offers a blogging and social networking platform where users can earn STEEM tokens based on the popularity of their posts and interactions.
- User Base: Steemit has a dedicated user base, primarily consisting of bloggers, writers, and cryptocurrency enthusiasts.
- Real-Life Example: Writers on Steemit can monetize their content directly through community engagement, earning tokens for high-quality posts and comments.
BlueSky
BlueSky is a decentralized social media initiative backed by Twitter, aimed at creating a decentralized standard for social media.
- Features: BlueSky focuses on decentralized identity and content management, allowing users to control their data and interactions across different platforms.
- User Base: Still in its development phase, BlueSky has generated significant interest from developers and users interested in decentralized social media.
- Real-Life Example: BlueSky aims to provide a platform where users can seamlessly move their identities and content across different social media networks, enhancing interoperability and user control.
Mastodon
Mastodon is a decentralized, federated social network that operates as a collection of independently run servers (instances) that communicate with each other. This model allows users to choose or create instances that align with their preferences and policies, promoting a diverse and inclusive ecosystem.
- Features: Mastodon provides microblogging capabilities similar to Twitter, with a focus on user control and community governance. Users can post “toots” (similar to tweets), follow other users, and interact with content across instances.
- User Base: As of early 2024, Mastodon has over 4.4 million users across its network of instances. Its decentralized nature allows for niche communities to thrive, each with its own moderation rules and policies.
- Real-Life Example: An instance like mastodon.social, one of the largest and most popular, provides a general-purpose environment where users can engage in a wide range of discussions and activities.
D.Tube
D.Tube is a decentralized video-sharing platform built on the STEEM blockchain, designed as an alternative to YouTube. It emphasizes censorship resistance and direct monetization for content creators.
- Features: D.Tube offers features such as video uploads, viewing, commenting, and upvoting. Creators earn rewards in the form of STEEM tokens based on the engagement their content receives.
- User Base: While specific user numbers are not as prominently reported as centralized platforms, D.Tube has a growing community of content creators and viewers, particularly within the blockchain and cryptocurrency niches.
- Real-Life Example: Creators who face demonetization or censorship on YouTube have migrated to D.Tube, where they can freely share their content and earn directly from their audience.
Mirror
Mirror is a decentralized publishing platform that leverages blockchain technology to allow writers to monetize their content through crypto-social media tokens. It offers a transparent and equitable environment for content creators.
- Features: Mirror provides tools for writers to publish articles, essays, and other written content. Users can mint their content as NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens), enabling unique ownership and trading opportunities.
- User Base: Mirror has attracted a diverse group of writers, journalists, and content creators interested in the intersection of blockchain technology and content creation. The platform is particularly popular among crypto enthusiasts and thought leaders.
- Real-Life Example: Notable blockchain advocates and influencers use Mirror to publish exclusive content and engage directly with their audience through token-based incentives.
BitClout
BitClout is a decentralized social network where users can buy and sell tokens representing influencers, blending social interaction with cryptocurrency trading. It operates on its own blockchain, combining elements of social media and decentralized finance (DeFi).
- Features: BitClout allows users to create profiles, post updates, and engage with content. The unique aspect is the ability to invest in “creator coins,” which represent the social capital of influencers and content creators.
- User Base: BitClout has seen rapid growth, attracting thousands of users and notable personalities within the crypto space. It offers a novel way to monetize influence and engagement on social media.
- Real-Life Example: Influencers with significant followings can see their creator coin values increase, providing a direct financial incentive tied to their popularity and engagement on the platform.
| Platform | Key Features | User Base | Unique Selling Points |
| Lens | NFT-based profiles, blockchain social interactions | Rapidly growing | Verifiable identities, profile portability |
| Steemit | Blogging, cryptocurrency rewards | Dedicated crypto community | Monetization through community engagement |
| BlueSky | Decentralized identity, content management | over 3 million users | Enhanced user control and interoperability |
| Mastodon | Federated instances, microblogging | over 10 million users | User control, community governance |
| D.Tube | Decentralized video sharing | Growing community | Censorship resistance, direct monetization for creators |
| Mirror | Decentralized publishing, NFTs | Diverse group of writers | Transparent monetization, blockchain integration |
| BitClout | Social interaction, cryptocurrency | Thousands of crypto users | Creator coins, social capital monetization |
These platforms exemplify the diverse applications and potential of decentralized social media. By addressing privacy concerns, promoting user autonomy, and offering innovative monetization models, they provide a compelling alternative to traditional social networks. As these platforms continue to evolve, they are likely to attract a broader audience, driving the adoption of decentralized social media in the mainstream digital landscape.
Challenges and Drawbacks
While decentralized social media networks promise significant advantages, several challenges and drawbacks impede their widespread adoption. Here’s a closer look at the primary issues:
Limited Popularity and User Base
Despite their potential, decentralized social media platforms have not yet achieved significant popularity, accounting for less than 1% of the total social media user base. The concept of decentralization alone is not compelling enough for the average user, who is often more concerned with ease of use and content availability.
User Experience Challenges
The complexity of blockchain technology presents a significant barrier to adoption. Users often need to manage private keys, wallets, and understand blockchain concepts, which can be intimidating. Additionally, many decentralized platforms lack the polished interfaces and seamless user experiences provided by centralized social networks, further deterring potential users.
Incorrect Incentives for Companies
Decentralized networks allow users to own and port their data across platforms, reducing the incentive for companies to invest in long-term development. Unlike centralized platforms that monetize user data, decentralized networks need alternative revenue models that do not rely on exploiting user information.
Financially Motivated Early Adopters
Many early adopters of decentralized social networks come from the cryptocurrency ecosystem, driven by financial incentives rather than a genuine interest in building a sustainable community. This focus on quick financial gains can undermine the network’s growth and stability, as these users may quickly move to the next lucrative opportunity, leaving behind a fragmented user base.
Scalability Issues
Decentralized networks face significant scalability challenges. The distributed nature of these platforms can lead to slower performance and higher latency compared to centralized networks, affecting the overall user experience. Additionally, scaling a decentralized network requires substantial infrastructure improvements, which can be resource-intensive.
Future of Decentralized Social Media
Despite the challenges, the future of decentralized social media holds significant promise, driven by technological advancements and evolving user needs. Here’s a detailed look at the potential developments and trends:
Growth and Mainstream Adoption
Continuous improvements in blockchain technology and user experience will pave the way for mainstream adoption of decentralized social media platforms. As these platforms become more accessible and user-friendly, they are likely to attract a broader audience.
Innovations in Decentralized Identity and Privacy
The development of decentralized identity solutions will enable users to control their digital identities securely, allowing seamless movement across platforms without compromising privacy. Emerging privacy technologies, such as zero-knowledge proofs and secure multi-party computation, will enhance user trust and attract privacy-conscious individuals.
Integration with Traditional Platforms
Traditional social media platforms are beginning to explore blockchain technology to enhance security, privacy, and user control. Integrations like Twitter’s Bluesky project aim to create decentralized standards for social media, potentially leading to hybrid models that combine the strengths of both centralized and decentralized networks.
Enhanced User Experience
Improving the user experience on decentralized platforms is crucial for their adoption. Developing intuitive and seamless user interfaces will lower the barrier to entry, making these platforms more accessible. Incorporating features like instant messaging, video sharing, and advanced content moderation tools will make decentralized platforms competitive with their centralized counterparts.
Final Thoughts
Decentralized social media represents a paradigm shift in how we interact online, offering enhanced privacy, user autonomy, and censorship resistance. Despite significant challenges, including limited user adoption, complex onboarding processes, and scalability issues, the potential for growth and innovation in this space is immense.
The key to driving the adoption of decentralized social media lies in creating a superior product. Blaize excels in developing user-friendly, secure, and innovative web3 solutions that can overcome these barriers. By focusing on improving user experience, leveraging technological advancements, and fostering community-driven governance, decentralized social networks can attract a broader audience and redefine the future of digital interaction.
The convergence of decentralized and traditional social media models will likely emerge, offering users the best of both worlds. With continuous innovation and a focus on user-centric design, decentralized social media has the potential to revolutionize the digital landscape, providing a more equitable and open online community. By embracing these networks, we can move closer to a future where users have greater control over their data and interactions, fostering a more secure and democratic digital environment.
Contact Blaize to discover new opportunities for your business based on web3 technologies!
