Public vs Private Blockchain: A Comprehensive Guide for Businesses
Surely almost any business needs a secure, transparent system to manage data. There are two options: a readily available public solution or building your private blockchain. Which one to choose and are there any pitfalls?
For many businesses, the answer isn’t as clear-cut as it seems. This guide delves into the world of public and private blockchains, providing a comprehensive exploration to help you chart the best course for your company.
Our exploration aims to dissect the nuances between these two blockchain paradigms, considering why the choice between them is not merely technical but strategic, influenced by a company’s specific needs, operational scale, and long-term vision.
The decision to adopt a public blockchain or invest in a private one is significant, shaping not only the immediate operational capabilities of a business but its future trajectory in the digital ecosystem.
Public blockchains offer a quick entry point into the blockchain world with established networks and protocols. However, for companies aiming for optimized performance, enhanced privacy, and bespoke solutions that align closely with their business model, a private blockchain becomes apparent. Despite the higher upfront costs and resource demands, the investment in a private blockchain can yield unparalleled advantages in efficiency, scalability, and competitive edge.
Let’s together take a closer look at the intricacies of private and public blockchains, their pros and cons, and their use cases.
What is a Blockchain?
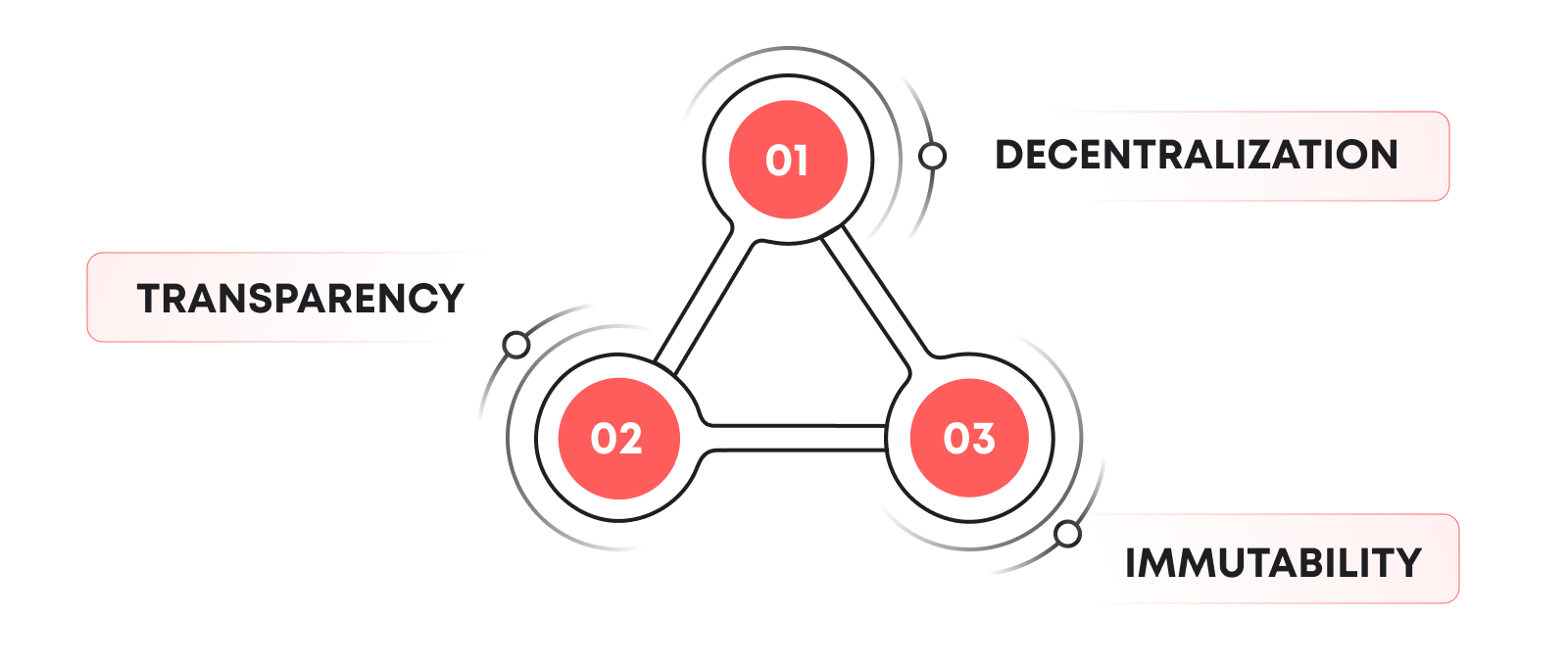
Blockchain technology is a decentralized ledger that records transactions across multiple computers. Its key attributes include:
- decentralization, which eliminates a single point of failure;
- transparency, allowing all participants to view the transactions; and
- immutability, ensuring that once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered.
Since its emergence alongside Bitcoin in 2009, blockchain technology has evolved significantly. Today’s networks often incorporate sophisticated layers and components or even utilize alternative data exchange models beyond the traditional “chain” structure.
This complexity underscores the growing need for expert teams. Raising a high-performing blockchain requires multi-profile specialists who grasp these intricate layers and navigate the ever-evolving landscape. Simply put, building a secure and efficient blockchain solution demands professional prowess beyond a basic understanding of blocks and hashes.
Whether you’re considering venturing into the blockchain space or simply seeking a clearer understanding, remember: the technology has matured far beyond its initial form. Embrace its depth and complexity, and consider seeking expert guidance to unlock its true potential for your needs.
Types of Blockchains
Understanding the different blockchain types is crucial for informed decision-making. While the underlying technology might seem similar, the access and governance models paint distinct landscapes. Let’s delve into the three main categories:
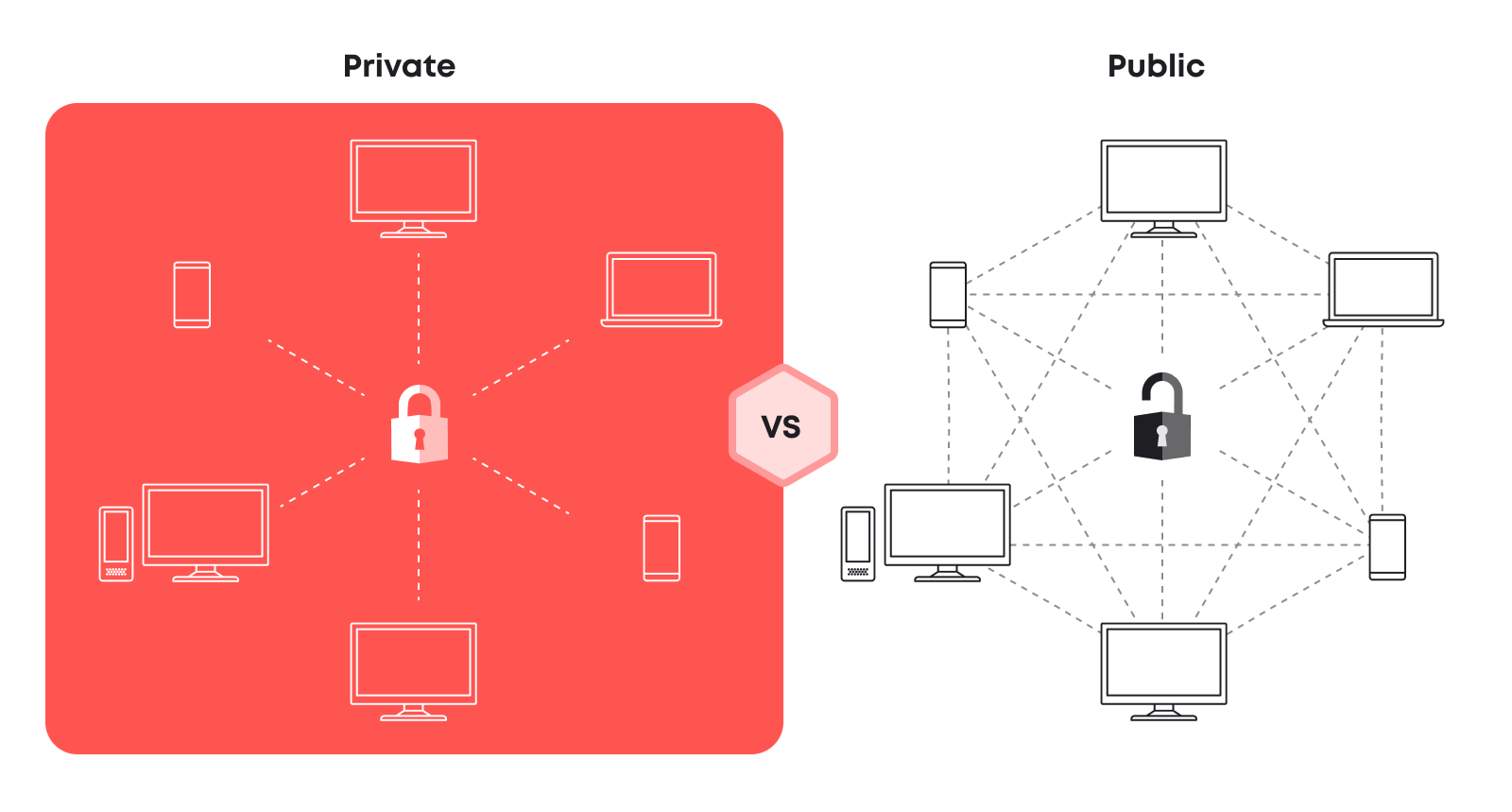
1. Public Blockchains: These open-access networks operate without a central authority. Anyone can join, participate in transactions, and access the complete ledger. Bitcoin and Ethereum are prominent examples.
2. Private Blockchains: Contrary to their public counterparts, private blockchains offer restricted access and permissioned participation. A single entity or a consortium governs the network, controlling who can join and interact. Examples include Hyperledger Fabric. At the same time, any open-source blockchain (like Ripple) may be forked and launched as a private one, accelerating the advantages of private and public networks.
Another great example of a private blockchain is one developed by Blaize for Radiologex. Get to know more details about the case further in the article.
3. Consortium Blockchains: Bridging the gap between public and private models, consortium blockchains involve a predefined group of organizations jointly managing the network. Each member retains control over its data while collaborating on shared processes. Examples include R3 Corda and Quorum.
Choosing the right private vs public blockchain depends on your specific needs. Consider factors like data sensitivity, regulatory requirements, desired level of control, and the nature of your collaborations. Understanding these distinctions is the first step to unlocking the transformative potential of blockchain technology for your organization.
Public Blockchains
Public blockchains thrive on openness and accessibility. Anyone can join and participate, fostering a level of transparency that builds trust across the entire ecosystem. This open door also fuels innovation, as anyone can contribute to the network’s development and growth. Security is another hallmark, with distributed consensus mechanisms working tirelessly to protect against fraud and unauthorized access. Additionally, public blockchains lower the barrier to entry for global economic participation, as anyone with an internet connection can join the playing field.
However, this very openness comes with its own set of challenges. Scalability can be an issue, particularly when dealing with large transaction volumes that can lead to slower processing times. Privacy concerns loom large, as all transactions are publicly viewable, potentially hindering the use of this technology for sensitive data. Finally, the evolving regulatory landscape surrounding cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology can create uncertainty for businesses looking to leverage this technology.
Private Blockchains
Private blockchains operate on permissioned networks, offering businesses a safe haven for managing data and transactions with a high degree of control and privacy. Unlike their public counterparts, they cater to customization and ensure data confidentiality. Businesses define the governance rules and manage access points, ensuring compliance with industry regulations and safeguarding sensitive information. Additionally, private blockchains are designed for specific user bases, allowing for faster transaction processing compared to public chains. This scalability makes them ideal for high-volume use cases within an organization.
However, the very features that empower businesses with control can also be seen as limitations. The centralized nature of private blockchains, relying on a central authority, can compromise some of the decentralization benefits that public chains offer. The closed nature might hinder rapid development and innovation, as participation is restricted to authorized members. Finally, dependence on specific vendors can limit flexibility and choice for businesses looking to explore different options within the blockchain ecosystem.
Consortium/Federated Blockchains
Consortium/federated blockchains bridge the gap between the public and private worlds, bringing together predefined groups of organizations in a shared network. This unique model offers a balance between control and collaboration, allowing trusted competitors or partners to work together while maintaining some control over data and operations. Transparency is ensured within the consortium, as authorized members have access to transaction details, fostering trust and accountability. Additionally, being designed for specific industry collaborations, these blockchains offer scalability and efficiency when processing transactions.
However, the trade-offs are worth considering. The predefined membership restricts participation to approved organizations, hindering broader ecosystem involvement and the potential for wider innovation. Managing a consortium can also be complex due to the need for multi-party governance and agreement on various aspects. Finally, similar to private blockchains, reliance on specific vendors can limit flexibility and choice for consortium members.
Comparing Public, Private, and Consortium Blockchains
When comparing these blockchain types, key considerations include access control, privacy, decentralization, scalability, and governance.
| Feature | Public Blockchain | Private Blockchain | Consortium/Federated Blockchain |
| Access Control | Open to anyone, with no restrictions on participation or access. | Restricted access, with permissions required to join the network. | Limited to several organizations, with access granted by consortium members. |
| Decentralization Level | Fully decentralized, with no central authority controlling the network. | Partially decentralized; central authority within an organization controls the network. | Semi-decentralized, with control shared among pre-selected entities. |
| Transaction Speed & Efficiency | Slower due to the consensus mechanism across a wide network. High latency in transactions can occur. | Higher, due to a reduced number of nodes. This leads to faster consensus and lower latency. | Varies, but generally optimized for efficiency through a limited and trusted node network. |
| Privacy & Confidentiality | Low privacy for transactions, as all data is public. Anonymity can vary. | High, due to controlled access. Transactions and data visibility are restricted to network members. | Customizable, with privacy levels adjustable according to consortium rules. Generally higher than public. |
| Security | High, with security ensured through extensive distribution and cryptographic algorithms. Vulnerable to 51% attacks theoretically. | Depends on the network’s security measures; potentially vulnerable to insider threats. | High, leveraging distributed trust models and potentially benefiting from combined security protocols. |
| Governance | Decentralized governance, usually through consensus algorithms like PoW or PoS. | Centralized governance by a single organization, allowing for quick decisions and updates. | Shared governance, with decisions made by a group of organizations according to consortium agreements. |
| Scalability | Faces scalability issues due to the consensus mechanism in a large network. Efforts like layer 2 solutions are in place to address this. | More easily scalable within its controlled environment due to fewer nodes and streamlined processes. | Scalability can be efficiently managed, depending on the consortium’s structure and technological framework. |
| Use Cases | Ideal for applications requiring transparency and security without censorship, like cryptocurrencies and public records. | Suited for internal business processes where privacy and efficiency are paramount, such as in supply chain management and confidential records. | Effective for cross-organizational processes where trust and privacy are needed among known entities, like in trade finance and healthcare data sharing. |
| Customization and Flexibility | Limited customization options for individual users; network upgrades require consensus. | Highly customizable to specific business needs, allowing for bespoke features and smart contracts. | Customization tailored to the consortium’s collective needs, balancing flexibility with shared control. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Challenging due to its open and global nature; compliance must be managed by users. | Easier to ensure compliance with data protection laws and industry regulations due to centralized control. | Designed to facilitate compliance across jurisdictions, reflecting the collective requirements of its members. |
Use Cases and Adoption
At its core, blockchain transcends a singular technology, evolving into a transformative architecture empowering diverse domains. Its unwavering promise lies in immutable data, seamless verification, and streamlined processes enabled by tokenization. Analogous to a versatile tool, its true impact unfolds through the lens of the individuals and entities wielding its potential.
Public Blockchain Use Cases
Imagine vibrant public blockchains like Avalanche and Ethereum as bustling marketplaces fostering open participation and innovation. Here, anyone can contribute and harness the network’s collective power. Let’s delve into real-world illustrations:
- Financial Democratization: Decentralized Finance protocols on Ethereum empower individuals to directly engage in lending, borrowing, and trading, circumventing traditional intermediaries. Envision peer-to-peer microloans facilitating financial inclusion or seamless cross-border transactions devoid of exorbitant fees.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Platforms like VeChain act as digital sentinels, tracking the journey of goods across continents with meticulous accuracy, ensuring their authenticity and ethical sourcing. Imagine farm-to-table traceability bolstering consumer trust or diamond provenance verification empowering informed purchasing decisions.
- Creative Empowerment: Artists and musicians leverage Ethereum’s robust infrastructure to mint and trade their work as unique NFTs, solidifying ownership and fostering direct interactions with fans. Imagine musicians receiving micro-payments every time their song is streamed or artists connecting directly with collectors for limited-edition artwork sales.
Blaize commitment to the public blockchain ecosystem extends beyond. Consider our ongoing work on the Web3 Foundation grant, a testament to our dedication to building solutions that benefit everyone.
For instance, our efforts focus on simplifying the node deployment process for networks like Polkadot, a public blockchain platform. By creating tools like Blaize’s unified deployment solution for collator nodes, we contribute to a stronger, more accessible infrastructure for the entire community. This idea aligns perfectly with the Web3 Foundation’s mission of fostering a decentralized and user-centric internet.
Remember, this is just one example of how our work benefits public blockchains and, consequently, everyone utilizing them. As we delve deeper into this transformative technology, we remain committed to developing solutions that not only address our client’s specific needs but also contribute to the wider public good.
Private Blockchain Use Cases
Envision businesses meticulously constructing their own secure networks akin to internal communication systems. Within these controlled environments, privacy, customization, and governance reign supreme:
- Healthcare Transformation: Hospitals leverage the secure haven of Hyperledger Fabric-based private blockchains to facilitate seamless sharing of patient data while upholding individual privacy. Imagine healthcare providers enjoying streamlined access to medical records, fostering collaborative care and improved patient outcomes.
- Manufacturing Optimization: Large corporations harness the transformative power of blockchain to weave transparency and efficiency into their supply chains. Picture automotive giants tracking parts movement in real-time, optimizing production schedules and minimizing costly delays.
- Trade Finance Reimagined: Consortiums of banks collaborate on private blockchains like R3 Corda to streamline trade finance processes, significantly reducing paperwork and expediting transactions. Imagine businesses enjoying faster access to funds and minimized costs associated with international trade.
Blaize has demonstrated profound expertise and a forward-thinking approach in the realm of private blockchain development, tailoring solutions that cater to the intricate needs of businesses seeking enhanced privacy, efficiency, and security. Our work encompasses a broad spectrum of industries, with notable projects in healthcare and technology sectors, exemplifying our ability to deliver customized blockchain solutions.
Architecture of Decentralized Layer for Radiologex
In the healthcare sector, Blaize spearheaded the development of a decentralized layer for Radiologex, a revolutionary platform designed to streamline and secure medical communications, data exchange, and collaboration.
This private blockchain infrastructure facilitates immediate, secure, and immutable data transactions, ensuring privacy and efficiency paramount to healthcare providers and patients. By integrating advanced cryptographic techniques and custom smart contracts, Blaize has enabled Radiologex to offer a robust, scalable platform that meets the stringent requirements of the medical industry.

Blockchain Data Hub Solution for R-DEE’s Integrated Health IT Suite
Another hallmark of Blaize’s expertise is the development of a blockchain data hub for R-DEE, integrating it with the company’s Integrated Health IT Suite. This solution leverages private blockchain technology to ensure secure data management, interoperability, and compliance with global healthcare standards. The platform supports seamless and secure data exchange across various healthcare services, enhancing patient care through improved data accuracy and availability.
These projects underscore Blaize’s commitment to leveraging private blockchain technology for solving real-world problems. Our team of multi-disciplinary experts harnesses the power of blockchain to design and implement secure, scalable, and efficient networks. Blaize’s approach combines deep technical knowledge with a keen understanding of industry-specific challenges, enabling us to deliver tailor-made solutions that enhance operational efficiencies, safeguard sensitive information, and foster innovation.
The Future of Enterprise Blockchains
The trajectory of enterprise blockchain technology is marked by evolving landscapes in both public and private networks, with distinct implications for business applications. As we delve into the future, the demarcation between public and private blockchains becomes increasingly nuanced, influenced by technological advancements, regulatory environments, and market demands.
Predictions for growth highlight a maturation of blockchain ecosystems, where the choice between public and private architectures is guided by strategic alignment with business objectives, rather than a one-size-fits-all approach.
A 2023 Gartner report predicts that 60% of global enterprises will explore or implement blockchain by 2025, highlighting the growing relevance of these open networks.
Scalability and Interoperability
A critical focus area in the evolution of blockchain technology is addressing the twin challenges of scalability and interoperability. These aspects are essential in determining the efficacy and applicability of blockchain solutions across diverse enterprise scenarios.
Scalability, or the ability to handle a growing amount of work or transactions, has been a bottleneck for many blockchain networks. However, ongoing developments, such as layer-2 solutions, sharding, and consensus mechanism innovations, are progressively enhancing the transaction throughput capabilities of both public and private blockchains.
Interoperability, the capacity for different blockchain networks to communicate and exchange data seamlessly, is another frontier being actively explored. The future promises an ecosystem where blockchains, irrespective of their underlying architectures, can interact without friction. This interoperability is crucial for building comprehensive, cross-industry applications that leverage the strengths of multiple blockchain networks. Initiatives like blockchain bridges, protocol standards, and cross-chain technologies are paving the way for a more interconnected and efficient blockchain landscape.
The advancements in scalability and interoperability are not just technical achievements; they represent a paradigm shift in how enterprises can deploy blockchain technology. By overcoming these limitations, businesses are poised to unlock unprecedented levels of efficiency, transparency, and collaboration. The future of enterprise blockchains, therefore, lies in creating agile, scalable, and interconnected networks that can support the dynamic needs of modern business ecosystems.
Conclusion
Public blockchains, with their open ecosystems and transparency, offer fertile ground for collaboration and innovation. Yet, scalability and privacy concerns might hold you back. Private blockchains, conversely, provide control, privacy, and customization tailored to your business needs, making it the best solution to drive your business’ growth and development. However, they restrict broader participation and potentially stifle innovation.
So, which path should you take? The answer, as always, lies in understanding your specific requirements and goals.
Building your own project? Consider two options:
1. Join the existing and mainstream ecosystem: Public blockchains like Ethereum or Solana offer established infrastructure, vibrant communities, and a wealth of resources. Leverage their existing capabilities and tap into the network effects of a thriving ecosystem. Remember, though, to carefully weigh scalability limitations and potential privacy concerns against the benefits of openness and collaboration.
2. Raise your own private blockchain: Opting for a private blockchain empowers you with complete control, customization, and privacy. This path is ideal for sensitive data, collaborative ventures within specific groups, or building applications requiring high transaction speeds and regulatory compliance. Be prepared, however, for the investment of building and maintaining your infrastructure and the potential limitations of a closed ecosystem.
Ultimately, the choice between public and private isn’t binary. Your blockchain journey might begin on a public chain, prototyping and testing your project in the open ecosystem. As your needs evolve and privacy or control become paramount, you can then migrate to a private realm, building your own tailored solution with Blaize experts.
Remember, blockchain technology is still maturing, and the landscape is constantly evolving. Embrace learning, explore both options and choose the path that best aligns with your current and future needs. With a clear vision and the right guidance, you can unlock the transformative potential of blockchain technology and build a solution that propels your business forward.
Don’t forget, our team of experts is here to help you navigate every step of the way. Whether you choose to join the public sphere or craft your own private blockchain, we can provide the knowledge, resources, and expertise to ensure your blockchain journey is a success.
FAQ
What are the key factors to consider when choosing between a public and private blockchain for a specific business application?
When deciding between a public and private blockchain for a business application, key factors include the desired level of privacy, the necessity for control over the network, scalability requirements, and the importance of transaction speed. Businesses must weigh the benefits of public blockchain’s transparency and decentralization against private blockchain’s enhanced security and efficiency to find a solution that aligns with their strategic goals and operational needs.
Which industries or domains are best suited for adopting public blockchains?
Industries that benefit most from adopting public blockchains include finance, for cryptocurrencies and DeFi applications; supply chain, for enhancing transparency and traceability; and governance, for secure and transparent voting systems. These domains leverage public blockchain’s strengths in security, transparency, and immutability to foster trust and streamline operations.
What are the major trends and outlook for enterprise blockchain solutions over the next 5-10 years?
The major trends and outlook for enterprise blockchain solutions over the next 5-10 years include a focus on scalability and interoperability, the integration of blockchain with other emerging technologies like AI and IoT, and a rise in consortium blockchains for collaborative industry solutions. Increased regulatory clarity and the development of more energy-efficient consensus mechanisms are also anticipated, driving broader adoption and innovation in blockchain technology across various sectors.
Contact Blaize to explore the opportunities of blockchain bridges right for your business!
